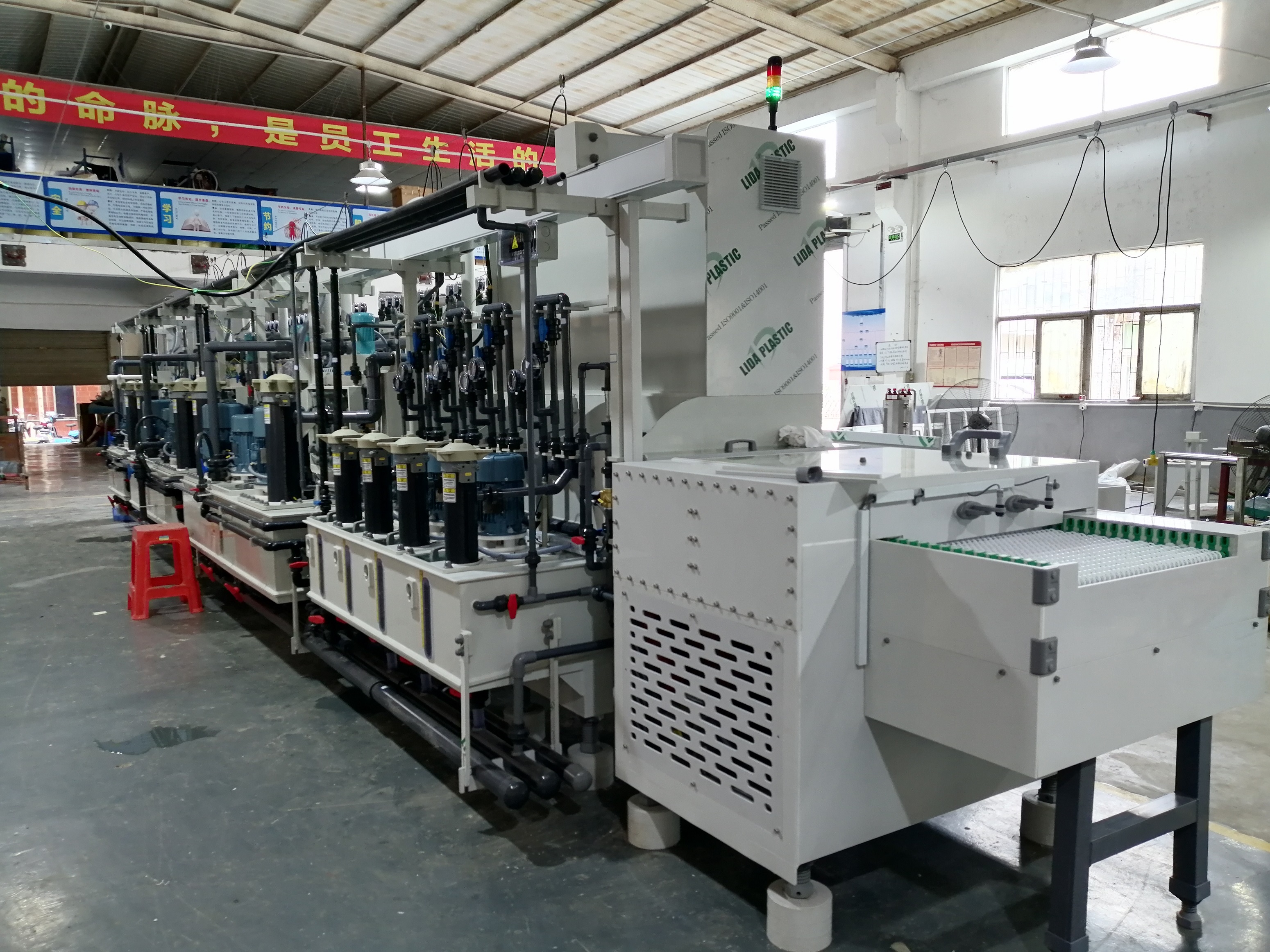
Electroplated copper layer has the advantages of good conductivity, thermal conductivity and mechanical ductility, and is one of the indispensable key electroplating technologies in the manufacture of printed circuit board (PCB).
Copper plating for printed circuit board includes Panel plating, graphic circuit copper plating and microporous fabrication copper plating. The commonly used plating solutions include sulfate plating solution, pyrophosphate direct plating solution and cyanide plating solution. At present, acid sulfate plating solution is commonly used.
The following is an example to introduce PCB copper electroplating technology.
I, Pickling
The purpose of pickling is to remove the oxides on the board surface and activate the board surface. Generally, the concentration is 5%, and some of them are kept at about 10%, mainly to prevent the unstable sulfuric acid content of the tank solution caused by the introduction of water.
During operation, it is necessary to control the pickling time, which shall not be too long to prevent oxidation of the board surface.
For acid solution, if the acid solution is turbid or copper content is too high after using for a period of time, it shall be replaced in time to prevent pollution to the surface of electroplating copper cylinder and plate. Generally, CP grade sulfuric acid shall be used as sulfuric acid for pickling.
2, Plating solution preparation
Acid copper sulfate bath has the advantages of good dispersion and deep plating ability, high current efficiency and low cost, which makes it widely used in PCB production.
Acid sulfate copper plating solution is generally composed of copper sulfate (CuSO4), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), hydrochloric acid (mainly acting as chloride ion Cl -), organic additives, etc.
Copper sulfate is the main salt and the main source of Cu2+ions in the solution. The concentration of copper sulfate should be controlled during preparation. If the concentration is too low, the deposition rate will be slow; if the concentration is too high, the deposition rate will be too fast, the crystal particles will be coarse, and the deep plating ability of the plating solution will be affected, making the thickness difference between the plate surface and the hole too large.
Generally, the content of CuSO4 • 5H2O is controlled at 60g/L~100g/L. The main role of sulfuric acid in the bath is to increase the conductivity of the bath and prevent the hydrolysis of Cu2+. The concentration should also be controlled during use.
If the concentration is too high, the dispersion ability of the bath is poor, but if the concentration is too low, the brittleness of the coating will increase and the toughness will decrease. In particular, it is necessary to keep ρ (H2SO4)/ ρ A proper and stable proportion of (Cu2+) can achieve a better deep plating effect.
According to practice, the content of H2SO4 should be controlled at 180g/L~220g/L. Chloride ion (hydrochloric acid) can improve the activity of the anode, promote the normal dissolution of the anode, and prevent anode passivation; It can also reduce the copper powder produced by incomplete anodic dissolution, improve the brightness and leveling ability of the coating, and improve the coating quality.
The content of chloride ion in the plating solution is generally low, which can be controlled at 30mg/L~80mg/L. Additives generally include carrier, brightener, leveling agent, etc. They play a very important role in acid copper sulfate electroplating. They can change the surface adsorption of the electrode, thereby changing the structure of the coating.
However, additives usually need several synergistic actions to achieve the desired effect. Therefore, it is difficult to accurately master the amount of additives in the actual preparation and electroplating process, which is also a problem in high-density PCB micro hole electroplating with high thickness diameter ratio. At present, foreign research has developed a technology that does not use additives by changing the conditions of pulse electroplating.
3, Panel plating
Also called one-time copper plating. Its function is to protect the thin chemical copper just deposited. Full board electroplating is to use the entire printed board as the cathode after hole metallization, thicken the copper plating layer to a certain extent, and then form a circuit pattern by etching to prevent the product from being scrapped due to the thin chemical copper plating layer being etched by the subsequent process. The control of process parameters related to full plate copper electroplating is as follows:
1.The main components of the bath solution are copper sulfate and sulfuric acid. The formula of high acid and low copper is adopted to ensure the uniformity of the thickness distribution of the plate surface during electroplating and the deep plating ability for deep holes and small holes; The content of sulfuric acid is generally 180g/L, most of which can reach 240g/L; The content of copper sulfate is generally controlled at about 75g/L.
2.A small amount of chloride ion shall be added to the bath solution to play a role as auxiliary luster agent and copper luster agent.
3.Copper polish shall be added according to the actual production board effect or the method of kiloampere hours. For example, copper polish shall be added according to kiloampere hours every day, i.e. 100ml/KAH~150ml/KAH. The amount of copper polish added or the amount of cylinder opening is generally 3ml/L~5ml/L, and the current of whole plate electroplating is generally calculated as 2A/dm2 × The electroplating area on the board, i.e. the board length (dm) for full board electroplating × Plate width (dm) × two × 2A/dm2。
4.The temperature of the copper cylinder shall be kept at room temperature, generally controlled at 22 ℃, not more than 32 ℃. If the temperature is too high in summer, the copper cylinder shall be equipped with a cooling temperature control system.
5.Check whether the filter pump works normally and whether there is air leakage; Clean the cathode conducting rod with a clean wet rag every 2h~3h.
6.The content of copper sulfate (once/week), sulfuric acid (once/week) and chloride ion (twice/week) in copper cylinder shall be analyzed regularly every week, and the content of polish shall be adjusted through Hall cell test to supplement relevant raw materials in time.
Attention shall be paid to safety when adding sulfuric acid. When adding large amount of sulfuric acid (more than 10L), it shall be added slowly in several times; Otherwise, the temperature of the bath solution will be too high, the decomposition of the polish will be accelerated, and the bath solution will be polluted; Special attention shall be paid when adding chloride ions. Because the chloride ion content is very low, it must be accurately weighed with a measuring cylinder or measuring cup before adding; 1ml hydrochloric acid contains about 385 chloride ions × 10-6.
In addition, the anode conducting rod and electric joints at both ends of the tank shall be cleaned every week, and the anode copper ball in the titanium basket shall be replenished in time, and the low current 0.2ASD~0.5ASD shall be used for electrolysis for 6h~8h; Check whether the titanium basket bag of anode is damaged every month, and replace the damaged one in time; Check whether there is anode mud at the bottom of anode titanium basket, and clean it in time if there is; The carbon core is used for continuous filtration for 6h~8h, and low current electrolysis is used for impurity removal; Determine whether to require major treatment (activated carbon powder) according to the pollution condition of the tank liquid every half a year or so; Replace the filter element of the filter pump every two weeks.



 Nov. 09, 2021
Nov. 09, 2021