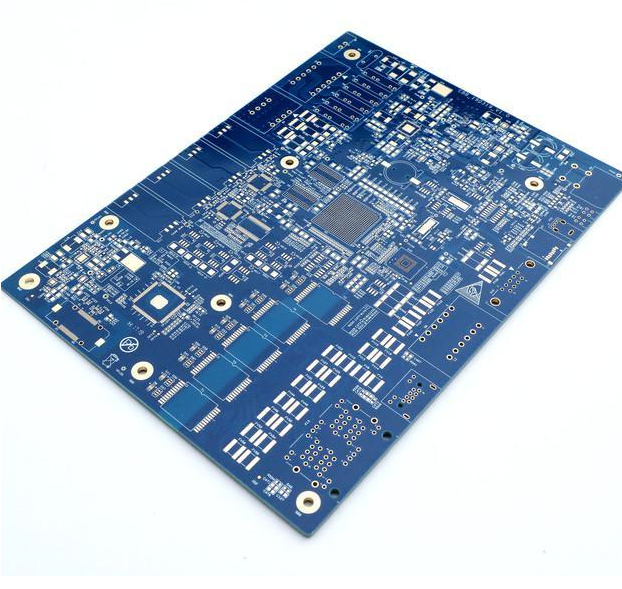
What does PCB proofing mean? Why PCB proofing? What is the function of PCB proofing? PCB proofing refers to that the designer has designed the drawings, but in order to ensure no mistakes and ensure the perfect performance of PCB, the test products, i.e. samples, will be made before mass production.
PCB proofing first needs to give the specific PCB data of proofing to the partner manufacturers. Take the PCB manufacturer as an example. First of all, we need to give the specific data of PCB proofing to the staff, who will quote the customers and the delivery cycle of products according to the specific data, process requirements and proofing quantity. If both parties think there is no problem, after both parties sign the cooperation contract, the staff will arrange the order and follow up the production progress.

First, the first step is material cutting. It is necessary to cut the board according to the data and design requirements provided by the customer, and cut the substrate material to the required size. After cutting, the substrate needs to be pretreated to remove the surface pollutants of copper film and improve the surface roughness, which is conducive to the subsequent film pressing process.
If the proofing PCB required by the customer is a multi-layer PCB, the inner layer shall be pressed first, and the copper surface of the finished substrate shall be pasted with an anti-corrosion dry film through hot pressing. Then, after exposure and development, the image on the original negative film is transferred to the photosensitive base plate through the action of the light source, and the dry film without chemical reaction is washed off with alkali solution, leaving the dry film with chemical reaction as the anti-corrosion protective layer during corrosion. The exposed copper after development is corroded by the drug solution to form the required inner line pattern.

After etching, the film needs to be removed, and the strong alkali is used to peel off the anti-corrosion layer on the protective copper surface to expose the circuit diagram. After the PCB proofing circuit is etched, it is necessary to check the inner layer, pick out the abnormal PCB for treatment, then punch through the CCD, and punch out the positioning hole and rivet hole of the detection operation with the CCD. The next step is AOI inspection and VRS confirmation. Using the principle of light reflection, the image is fed back to the equipment for processing, compared with the set logic judgment principle or data graphics to find out the abnormality. After connecting with AOI, the test data of each test version is transmitted to VRS through VRS, and the abnormality detected by AOI is confirmed manually.
After the inner board is confirmed to be correct, the next step is to press the copper foil, film and the oxidized inner circuit board into a multilayer board. After the pressing plate is finished, the copper surface needs to be browned and roughened. The surface area in contact with the resin on the copper surface is increased to increase the wetting of copper to the flowing resin, so as to blunt the copper surface and avoid adverse reactions. Then riveting is required, and multiple inner plates are nailed together with rivets to avoid sliding between layers in the subsequent processing process. After riveting, laminate the pre laminated floor into laminated multi-layer plate, and then press the laminated plate into multi-layer plate by hot pressing.

After the pressing is completed, the hole is drilled, and the through hole for the line connection between layers is drilled on the board surface. After drilling the hole is electroplating, so that the resin and glass fiber of the non-conductive part on the hole wall are metallized, and then the glue slag needs to be removed to expose the copper holes to be interconnected in each layer. Then, the outer layer needs to be treated, film pressed, exposed and developed, and then the secondary electroplating is carried out. The copper thickness is plated to the thickness required by the customer. After tin stripping, the line etching, AOI inspection and VRS of the outer layer are carried out. The more layers of PCB that customers need to proofing, the more pressing times and processes they need to perform.
After checking and confirming that each layer is correct, anti welding is required to achieve the purpose of anti welding, protective plate and insulation, followed by silk screen characters for maintenance and identification.

The final process is surface processing and testing. Of course, some customers will also have some special processes. In short, proofing is based on the specific information of customers.






 Nov. 17, 2021
Nov. 17, 2021